Assessing the needs of your candidates is essential for providers to determine how much to award and to whom. Some scholarship providers offer need-based scholarships that consider students’ financial needs among their eligibility requirements. Need-based scholarships are important because they offer support to students who may not have access to other forms of aid and help ensure access to education for students from lower-income backgrounds. If you aren’t awarding need-based scholarships, you shouldn’t need to collect financial data or assess financial needs. In this blog, we will provide strategies your organization can use to help assess the financial needs of applicants.
Guidelines for Collecting Financial Data from Students
Financial need assessment is critical for ensuring fairness and sustainability within your scholarship application. It’s important to find a balance between data collection and making applicants comfortable sharing their financial details. Here are some essential practices you should follow.
Limit Barriers by Building Trust
Use trust as the foundation of your need assessment process. Be transparent about how financial data will be used and explain each question’s purpose. Ask students for only the data you need, but not necessarily for verifications. Verifications can add time, introduce barriers, and may have a cost attached.
Ask Only the Essential Questions
When collecting financial data, ensure every question is purposeful and essential for selection. This should apply to any scholarship application, but especially to need-based programs, where financial questions should align with the eligibility or selection criteria.
Here are a few examples of purposeful financial questions:
- What is your household income?
- How many dependents are in your family?
- Do you currently receive any form of government assistance (e.g., SNAP, Pell Grant)?
These questions can offer meaningful insight to your organization without overwhelming the applicant. Additionally, try to avoid unnecessary details to keep the application clear and focused.
Be Clear and Concise
Eliminate jargon from questions, examples, and explanations. The financial portion of an application can be one of the most challenging for students to complete, so make it as simple as possible. This includes avoiding technical financial terms and using plain language that is accessible to all applicants.
Consider Alternatives to Verifications
Instead of requiring official documents, consider alternatives like self-reported data including broader income brackets or thresholds. You could also prompt students to use tools such as the Student Aid Index (SAI) estimator. The SAI can provide an estimated financial need level for students who may not qualify for FAFSA due to requirements such as citizenship status.
Determining Financial Need: Approaches for Providers
As a provider, it may seem challenging to assess the financial needs of candidates. Here are several approaches you can utilize to help.
Qualitative and Quantitative Responses
Start by assessing qualitative and quantitative responses in your application to understand a student’s financial circumstances. You might request financial information such as income, assets, household size, and more, but also allow space for qualitative details. For example, a section where students can explain their financial challenges can add helpful context.
Student Aid Index (SAI)
The SAI, provided through FAFSA or its estimator tool, is an effective resource for evaluation. This estimate helps establish a baseline understanding of a student’s financial need, including students who may not qualify for FAFSA but could still benefit from financial support.

Cost of Attendance and Unmet Need
By reviewing the cost of attendance figures from their university, you can calculate unmet need (cost of attendance minus gift aid received). Knowing the unmet need allows you to assess gaps in a student’s funding, helping you provide impactful support. Understanding tuition displacement is also important to determine how your program’s assistance may affect their financial need and award status from schools. You can learn more about how your students may be impacted here.
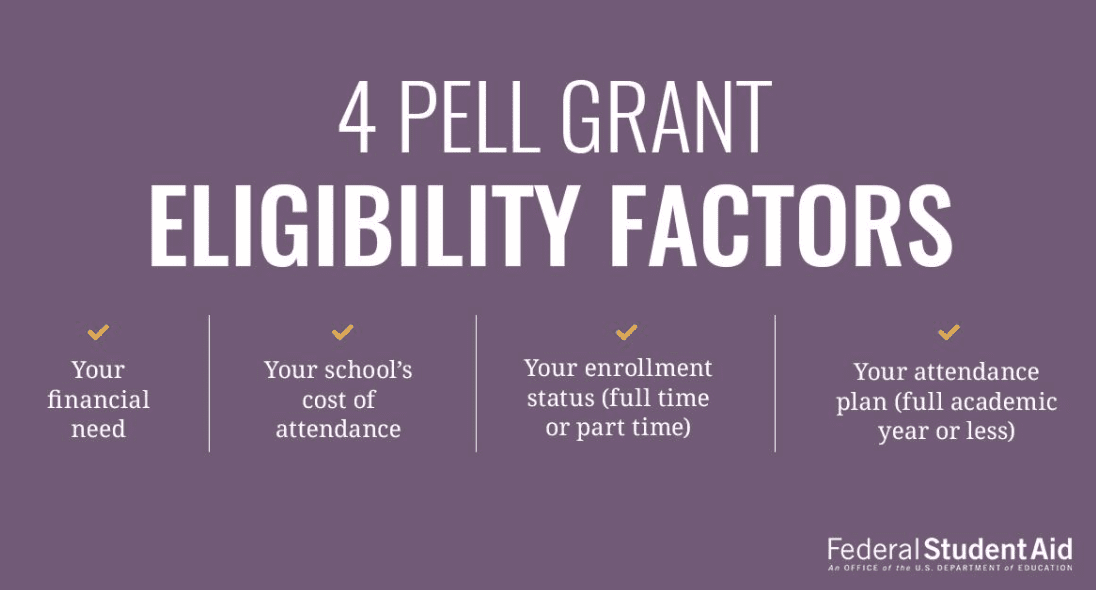
Eligibility for Pell Grants and Social Welfare Programs
Eligibility for programs such as Pell Grants or social welfare assistance can serve as an estimate of financial need. These indicators provide insight into a student and family’s financial situation, simplifying the guesswork.
Building a Financial Need Rubric for Assessments
When assessing applications for your need-based scholarship, consider creating a financial need rubric. This rubric can help you systematically evaluate each applicant’s financial situation. Since every student’s circumstances are unique, and qualitative responses can be subjective, a standardized process promotes fairness.
Define Your Criteria Across Categories
Set criteria across multiple categories relevant to financial need. Common categories include family assets, income, number of dependents, and any special circumstances. For instance:
Family Income: Score based on reported household income brackets.
Assets: Take into account significant assets, if disclosed.
Dependents: Adjust scoring based on the number of dependents in the household.
Special Circumstances: Include additional points for situations like medical expenses or single-parent households.
Develop a Consistent Scoring System
Make sure to create a scoring system that applies equally to all applicants. Each category should have its own scale, allowing you to assess each component of need consistently. This approach ensures that each factor contributes fairly to the overall need assessment.
By implementing these strategies, you can create a fair and accessible process for assessing the financial needs of scholarship applicants. Prioritizing simplicity, clarity, and trust will help encourage students to complete applications with confidence, enhancing your program’s impact.